
OSDP: The Only Secure Access Control Option
OSDP: The Only Secure Access Control Option
Access control technology has come a long way from the very first method of “Knock, knock!” “Who’s there?” to becoming an integrated network application within an intelligent building. In the early 1970’s access control moved to being electronically controlled, but still somewhat siloed with the primary function to create barriers from unauthorized persons. With the introduction a smartphone in 2007, security moved to being controlled and monitored on a remote device, connected to the Internet. Access control systems included both mechanical and electronic hardware devices from basic physical keys and door locks spanning to advanced access control systems encompassing IP features such as biometrics. As we return to our places of work, a new purpose of access control is emerging to include promoting wellness of inhabitants in addition to safety. Today almost every commercial and residential building employ some sort of electronic access control system and is a collaboration between IT and physical security.
According to ANSI/BICSI-007-2020 standard, “Information Communication Technology Design and Implementation Practices for Intelligent Buildings and Premises,” the components of an access control system are classified into the following levels:
- Level 1 – Central equipment processing, recording, software, and database
- Level 2 – Controllers for intelligent field processing (e.g., data gathering panel)
- Level 3 – Peripheral devices (e.g., card reader, lock, door position switch)
- Level 4 – Credentials (e.g., cards, fobs, biometrics, personal identification numbers [PINs], passwords)
All of these can be integrated into the data network to provide a complete integrated access control system. Connectivity to edge devices, such as peripheral devices allow sensors to monitor and control passage through entryways. These devices are classified into these categories:
- Door contacts—used for monitoring an open or closed door.
- Readers
- Electrified door hardware
- Request-to-exit devices (REX)
COVID-19 also seems to be accelerating the shift in access control to become mobile and cloud-based solutions. However, the merging of physical and logical access control systems still face many challenges that impede the journey to a truly digital infrastructure. Designing and implementing a network-based access control system includes assuring that the installed infrastructure utilizes the most secure cabling with advanced security and IP communication capabilities, in addition to being able to update and integrate with other devices.
OSDP as the New Gold Standard for Access Control
The Security Industry Association (SIA) industry introduced the Open Supervised Device Protocol (OSDP) as the essential standard for access control communications to enable digital access control features with advanced data encryption.
It’s easy to see understand why OSDP has become the security industry’s gold standard replacing old Wiegand-based systems and wiring protocols. Prior to OSDP there was a disconnect between the multiple device components including the readers, hardware, door contacts and controllers. OSDP has advanced functionality and provides a roadmap to future access control devices.
Wiegand dominated the access control industry for decades but hasn’t kept up to today’s requirements for many critical functions such as secure encryption, which is vital to protect against intercepting transmissions between proximity cards and readers. Wiegand offers only one-way communication, which becomes vulnerable to “sniffers” and hackers, whereas OSDP has bi-directional communications and supports AES-128 encryption, as used in federal government applications. This prevents hackers from intercepting data transfers. With bi-direction communication, access control systems are continuously monitored to protect against failed, missing, malfunctioning or tampered readers. OSDP utilizes the RS-485 protocol for the cabling and facilitates longer distances and is more robust to mask interference.
There are even more reasons to make a move to OSDP. Wiegand readers require homerun pulls from the control panel to each peripheral device. OSDP has a concept called “multi-drop” that allows devices to daisy chain directly from the controller to the reader and then to a secondary reader and so on. This reduces the number of ports on the controller, as well as the number of individual cable runs, saving on cabling and installation time. OSDP requires as few as two pairs compared to 6-12 (or more) conductors used in Wiegand. In addition, OSDP works with biometric devices and allows for remote configurations and upgrades, while Wiegand employs time-consuming workarounds.
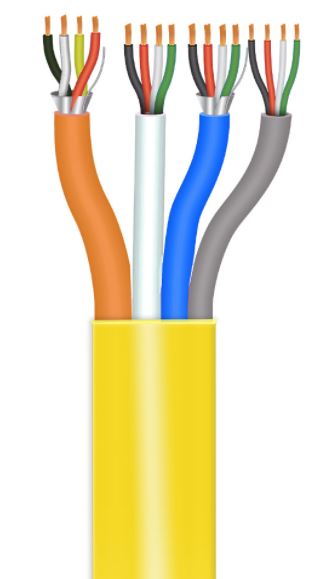 Composite OSDP Access Control Cable by Paige
Composite OSDP Access Control Cable by Paige
Connecting with Paige OSDP Cable
Recently Paige introduced a family of OSDP composite cables for today’s most advanced access control systems utilizing the OSDP protocol. The low-capacitance card reader component allows for distances to extend out to 4,000’ versus being limited to 500’ with Wiegand. In addition, to having fewer wires OSDP leverages the bi-directional communication to allow for simplified remote upgrades and configurations not possible with Wiegand systems. Because these are based on OSDP standards, they can easily integrate with other building systems like video or gunshot detection.
The Paige OSDP reader cable consists of 2 pairs of 24 AWG stranded bare copper cable with an overall tinned copper shield and a low-smoke PVC plenum-rated jacket. Meeting RS-485 communication protocols this cable is available in 1000’ lengths.
The composite cable consists of four components that are cabled together with an overall yellow jacket. The cable is rated to a 75°C operating temperature and meets UL-444 plenum rating and is available in lengths of 500’ and 1000’. Cables can be spliced together to extend the distance. The individual cable components are color-coded to allow easy application identification. The components include:
- Component 1: Reader - Orange inner jacket, shielded with 24 AWG/2 conductors;
- Component 2: Contacts - White inner jacket, unshielded with 22 AWG/4 conductors;
- Component 3: REX/Power - Blue inner jacket, shielded 18 AWG/4 conductors;
- Component 4 - Lock Power or AUX: Gray inner jacket, unshielded 18 AWG/4 conductors.
If you want to make sure your access control system is integrated into your intelligent building to deliver the highest security capacities, contact Paige: https://www.paigedatacom.com/osdp

